Creating Financial Security For Future Generations
The world economy is facing considerable challenges, and many are wondering whether they can pay their bills, let alone save for the future. The Financial Times compares it to the twilight zone: “the point between someone dying and their estate being distributed.”
Death in a family can be an opportunity to save significant sums in tax through clever navigation of the system. But options such as these are only for the fortunate few with something to inherit.
It may seem like an uphill struggle, but even in financially turbulent times, there are ways to ensure a future for yourself and the generation to follow.
Trust funds And ISAs

Investopedia defines a trust fund as:
“Trust funds are legal entities that provide financial, tax, and legal protections for individuals. They require a grantor, who sets it up, one or more beneficiaries, who receive the assets when the grantor dies, and the trustee, who manages it and distributes the assets at a later date.” – Investopedia
There are many types of trust funds in the US, so that the options can seem overwhelming. It’s best to consult with a financial advisor to narrow your options or investigate whether there’s an entirely different avenue to consider. Your choices will depend entirely on your financial circumstances:
- Asset Protection: This fund protects a person’s assets from their creditors’ future claims.
- Blind: This fund tries to remove any hint of conflict of interest. The trust fund’s grantor and beneficiary do not know about the holdings or who manages them. It does, however, give control to the trustee.
- Charitable: A charitable trust fund benefits a charity or the general public, including a Charitable Remainder Annuity Trust (CRAT) that pays a fixed amount each year. A Charitable Remainder Unitrust passes assets to a specified charity, giving the donor a charitable deduction and a fixed percentage of income to the beneficiary.
- Generation-Skipping: This one contains tax benefits when the beneficiary is one of the grantor’s grandchildren or anyone at least 37½ years younger than the grantor.
- Grantor Retained Annuity: Establishing this fund allows the grantor to transfer any appreciation of assets to any beneficiaries to minimize estate taxes.

- Individual Retirement Account: Trustees control IRA distributions rather than the beneficiaries.
- Land: This allows for property management, such as land, a home, or another type of real estate.
- Marital: This is funded at one spouse’s death and is eligible for the unlimited marital deduction.
- Medicaid: Designed to allow individuals to set aside assets as gifts to their beneficiaries, this enables the grantor to qualify for long-term care under Medicaid.
- Qualified Personal Residence: An individual can move their personal residence from their estate to this type of fund to reduce the amount of gift tax incurred.
- Qualified Terminable Interest Property: This one benefits a surviving spouse but allows the grantor to make decisions after the surviving spouse’s passing.
- Special Needs: People who receive government benefits are the beneficiaries so as not to disqualify the beneficiary from such government benefits.
- Spendthrift: Beneficiaries don’t have direct access to the named assets, which means they can’t sell, spend, or give away the assets without specific stipulations.
- Testamentary: This fund leaves assets to a beneficiary with specific instructions following the grantor’s passing.
Holistic planning
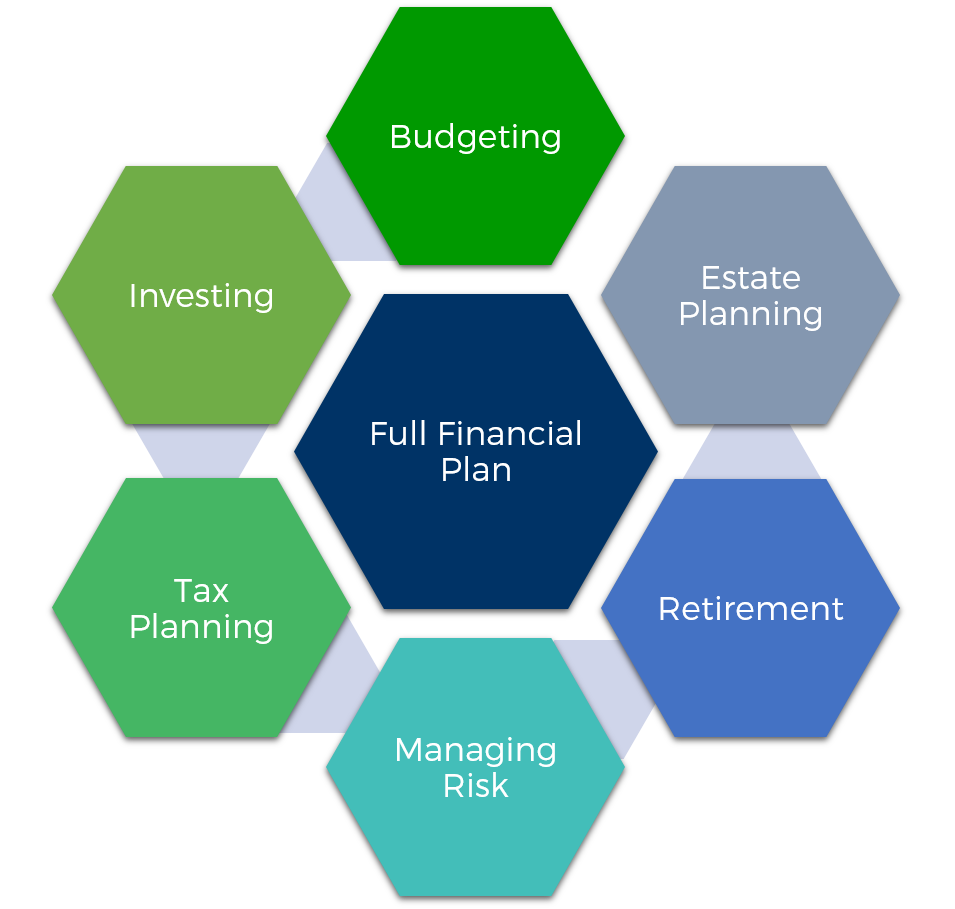
“Holistic Financial Planning looks at all aspects of your personal and financial life, before creating a plan for your money. It takes into account where you are today, where you want to be and then creates a plan to help you get there.” – Frazerjames
‘Holistic’ is the buzzword of the moment. However, it means taking the big picture and creating a comprehensive financial plan. Most traditional financial advice centers on only one aspect of your finance, e.g., savings, investments, tax, or insurance.
There are four steps to a holistic approach:
- Goal Setting
- Financial Check
- Financial Planning
- Action Planning

A holistic financial plan can include the following:
- Investment strategy, including investments made through taxable brokerage accounts
- Retirement planning through a 401(k), Individual Retirement Account, or tax-advantaged account
- Social Security and Medicare benefits planning
- Discussions around annuities to create a reliable income
- Long-term care planning, including the use of long-term care insurance
- End-of-life planning, including the need for advance healthcare directives or power of attorney
- College planning
- Insurance planning, including life insurance and disability insurance
- Estate planning
- Tax preparation and planning
- Budgeting
- Saving for short- and long-term financial goals and needs
- Business and succession planning
- Charitable giving
- Significant life changes, such as a divorce, job loss, or birth of a child
Invest, Wisely

We’ve all heard of generational wealth, and many view it as an inheritance only for the super-wealthy. There are steps we can take to get the ball rolling, however, which doesn’t mean becoming a millionaire overnight.
According to Bloom Money, there are five main strategies you can use to invest in your children’s future:
- Saving money
- Investing in stocks and shares
- Buying real estate
- Planning education
- Building a business
Stocks And Shares

Long-term investments are a successful way to build wealth. In contrast to building savings in a bank account, there is no guarantee with investments; stocks and shares increase in value over time. So by setting up an Individual Savings Account (ISA) or investing in stocks and shares through another means, you can grow your wealth over many years.
You do need to be prepared to play the long game. Investment markets fluctuate, so you should commit to long-term investments to see the best returns.
Real Estate

Holdings in commercial property consistently outperform other asset classes. The three main types of property investment are:
- Commercial
- Residential
- Agricultural
Of course, only invest in property if you have the funds to do so, don’t put yourself in debt trying to build a property portfolio. However, it’s an excellent investment if you can purchase property and either provide a rental property or flip it for a profit.
The more money you put down on the house, the less you will have to pay in interest later. But once everything comes together, real estate is a good investment that guarantees passive income and tax advantages.
Deal With Your Debt

Nearly 80% of American households are in debt, and the average debt due to every American citizen is around $38,000. It’s challenging to get out of the hole due to high-interest rates, but to secure your family’s financial future, you must eliminate all forms of debt within your lifetime.
Paying off any outstanding debts can free up capital for investment and provide a shield against market fluctuations. If you have any outstanding loans, pay them off as soon as possible so that future generations don’t have to bear the burden when you’re gone.
You can start by paying off high-interest loans and credit card bills outstanding. By siphoning off portions of the debt every month, you can ensure the interest rate on those debts also comes down.
Educate The Next Generation

Educating them in financial responsibility is a less obvious method of providing financial security for future generations. Many young people don’t feel like they have the knowledge or tools to manage their finances effectively, and fewer still completely understand investment and business tactics.
There are many different ways children can learn about the value of money.
- Involve your children in charitable endeavors to inculcate values of giving, compassion, and rational spending.
- An allowance with restrictions teaches kids how to save, spend, and manage their money effectively. However, if you give your child a free hand in terms of spending, there’s a chance they’ll spend it frivolously on inessential objects or activities. Set up rules that limit how much money they can spend each week or month, so they save and shop only for the essentials.

It’s also a good idea to open a bank account with them early on and teach them how interest works, the benefits of building interest, and how they can continue to save as they grow. Educate young people on debt management and how a credit score will affect the rest of their lives. The sooner they understand, the better prepared they will be for the difficulties of student loans, credit management, and mortgage applications.
Conclusion
We have the burden of living in interesting times, and there’s no avoiding the challenging financial realities we live in now and inevitably await upcoming generations. However, we can plan and use our resources to provide some stability for the children and grandchildren we love.

There is no easy solution. If you are fortunate enough to have built a successful career or have inherited wealth to pass on, that’s a great place to be. For those with fewer means but as much desire to provide financial aid to their loved ones, careful planning, and a considered approach are key.
Never spend money you don’t have. Invest wisely. And always seek financial advice before making any big changes.